Researchers devise a “5D” method for storing 500TB of data on a CD-sized glass disk
In the current age where information and data are increasing at an unexpected pace, the need for massive storage devices such as a hard disk drive and a Compact device for storing 500TB of data is now more than ever before. Fortunately for us, researchers around the world are making great progress in providing large storage spaces in compact disks
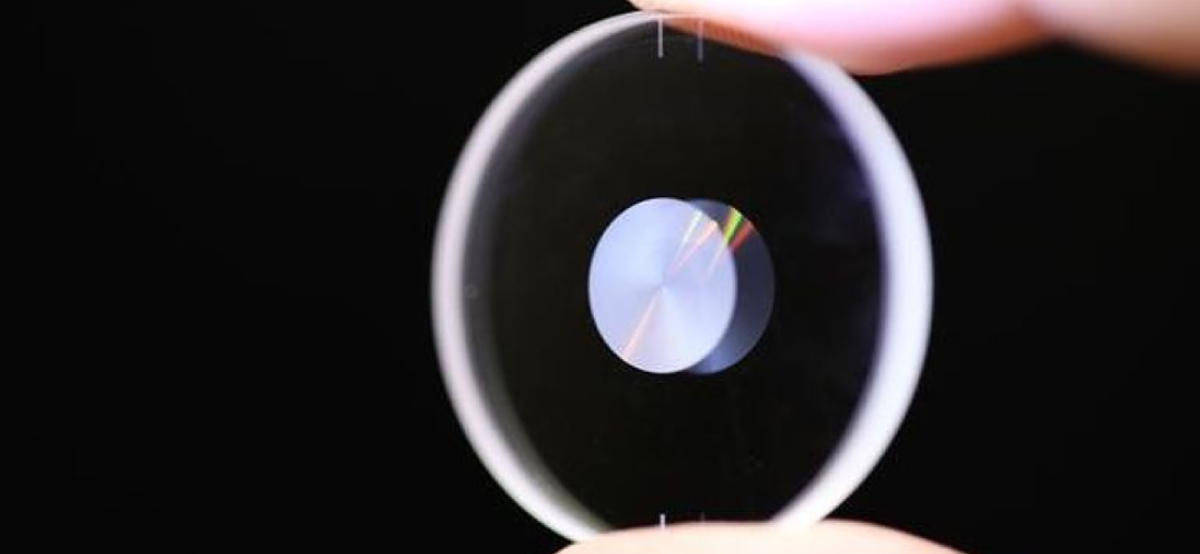
Recently Optica has confirmed that a group of exceptional researchers at the University of Southampton in the UK have managed to develop an efficient high-definition nanostructure in a silica glass that works efficiently on laser-writing method. The development of such a device would not only extend the storage but also is an easier way to carry a portable massive storage device that comes in the form of a CD.
What is the 5D 500TB CD-Sized Glass Disk?
The device is an innovative model designed to solve low storage problems. The device uses a five-dimensional method that can be used for storing 500TB of data on a CD-sized class disk. The high-density device can be used for storing long-term data and is 10,000 times denser than a Blu-Ray optical disk.
This new writing method for data decompresses three spatial dimensions and two optical dimensions that add effectiveness and efficiency to his device.


What Benefits Does the Device Offer?
Individuals and organizations are now creative massive data sets that require more storage in the form of efficient devices and a slow-performing hard disk drive is no longer cutting it. Therefore, the introduction of 5D glass disks would help businesses that require compact devices for storing a large amount of data. This device offers a high capacity, efficient performance, low-energy consuming and a long life span.
Doctoral Researcher Yuhao Lei from the University of Southampton also commented that Cloud-based systems are designed in a way to keep data temporarily and 5D data storage in glass is a device that would be best for storing long-term data. Long-term data might include data for museums, National archives, and libraries.
How Does Laser-Writing Work?
The new laser-writing approach allows the device to write at the speed of 1,000,000 voxels per second. It is quite a high speed that is equivalent to recording 230 KB of data per second. The laser-writing of birefringence structures inside a silica glass features a polarizer. A polarizer can be defined as an optical filter that blocks light waves from other polarizations and lets specific light of polarizations pass through it.
The polarizer works as a schematic of a laser writing setup. It also features an Electro-Optic Modular and a Quarter Wave Plate. The speed of the device isn’t spectacular but the new technology it brings to the table isn’t the s [peed, as it’s the immense storage capacity of 500TB. Nevertheless, it is still a pretty good upgrade in terms of speed as compared to the older technology.
This device may not be the first when talking about 5D silica glass disk but it is the best one. Even though there have been previous approaches but they couldn’t make the cut because of insufficient density or writing speed. The researchers were able to overcome this challenge by femtosecond laser along with a high repetition rate that resulted in creating tiny pits containing a structure similar to a Nano-lamella that were measured to be 500X50 nanometers each.

The Generic Physical Mechanism:
It is anticipated that the 5D silica glass disk’s energy-efficient laser-writing method can be used for speedy Nano-structuring in transparent materials for 3D integrated applications for microfluidics and optics. All this can be possible because the disk feature is a generic physical mechanism.
One of the primary reasons behind the efficiency of the disk is the fact that the Nano-structures are anisotropic. This is why they produce birefringence that can be characterized by the slow axis orientation of the light and strength of retardance.
The slow axis orientation and the strength of retardance can be controlled by the intensity of light and the polarization respectively, once the data is recorded into the glass. With the help of localized Nanostructures, the capacity is increased, and with the use of pulsed light, the energy consumption required for writing is reduced as a result.
Technology Testing On 5GB Silica Glass Disk:
The research team used the same writing technology on a 5GB glass disk, which is the same size as a standard CD. However, using this technology meant that it was possible to store 500TB of data inside the 5GB disk. It is estimated that an upgraded system that supports parallel writing would take about 60 days to write such a huge amount of data.
With that being said it would take a significant and prolonged amount of time to write terabytes of data with the current systems we use. Currently, researchers are finding new ways to improve the writing speed of the disk to make it practically usable outside laboratory settings.
Conclusion:
The 500 TB silica glass disk is undoubtedly an innovation for storage devices, as a hard disc drive has evolved and now we are seeing the evolution of CDs. Although the writing speed of the disk isn’t quite much it is a useful device that will be improved over time for better efficiency.
Researchers are making sure to add more and more upgrades to the disk that would increase its performance and practicality of use. More and more organizations require such devices and will indeed benefit from this 500 TB silica glass-like disk.